MBTI, short for Myers-Briggs Type Indicator, is a personality metric developed by and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers, based on Carl Jung’s theory on psychological types. Carl G. Jung introduced in the theory of psychological types in the 1920s by. Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter, Isabel Briggs Myers, developed the MBTI tool in the 1940s. Millions of people worldwide have taken the Indicator each year since its first publication in 1962.
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
The original goal of MBTI was to improve the lives of working people by providing a rational basis for aligning people with jobs. It was designed to be used as a placement tool, a convenient and easy-to-use method for sorting employees in ways that maximized their happiness and the productivity of organizations.
Today, it is a common tool used by individuals and organizations alike, be it to better understand themselves or to optimize workplace dynamics.
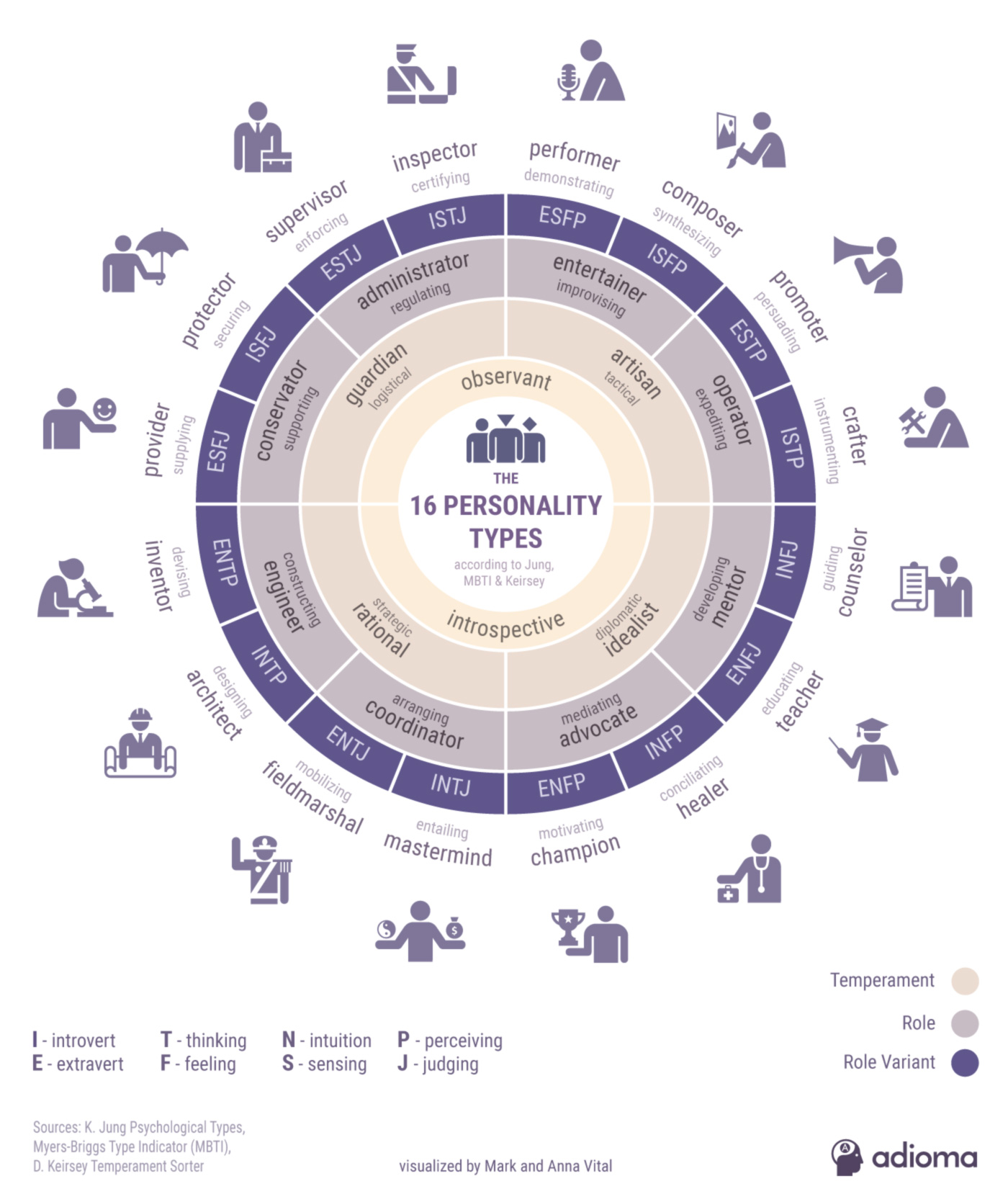
Personality Types
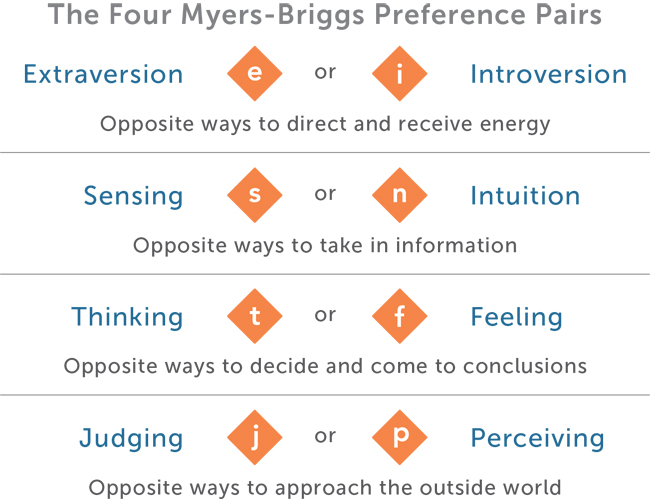
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) classified people into four personality types:
- Extraversion / Introversion
- Sensing / Intuition
- Thinking / Feeling
- Judging / Perceiving
Extraversion vs. Introversion
The traits of extroversion and introversion are a central dimension in some human personality theories as the MBTI assessment. Generally, people who prefer to direct their energy outwards – to people, things, situations – are extroverts (E). Contrarily, people who prefer to direct their energy inwards – to ideas, information, beliefs – are introverts (I). Extroverts are action-oriented, while introverts are thought-oriented. An extrovert prefers to focus on other people and things. The introvert, however, prefers to focus on internal thoughts and ideas.
Sensing vs. Intuition
People who prefer to deal with facts, details, and concrete information are sensing types (S). People who prefer to deal with ideas, abstract concepts, and theories are intuitive types (N). The sensing person prefers to use the five senses to receive information. The intuitive person, however, receives input from internal thinking processes.
Thinking vs. Feeling
People who prefer to make decisions from a detached standpoint, using reason and logic to make conclusions are thinking types (T). People who prefer to make decisions from an insider, emotional standpoint are feeling types (F). The Thinking person judges using logic, while the Feeling person uses affective measures to judge.
Judging vs. Perceiving
People who prefer a planned, well-structured life are judging types (J). Whereas, people who prefer to go with the flow are perceiving types (P). Correspondingly, the judging aspect of the type results in sequential step-by-step mental processing. In contrast, the Perceiving person responds in a spontaneous and flexible way.
In total, there are 16 personality types. For example, someone who is ENFJ means that this person is Extroverted, iNtuitive, Feeling and Judging. So, each personality type indicates a preference.
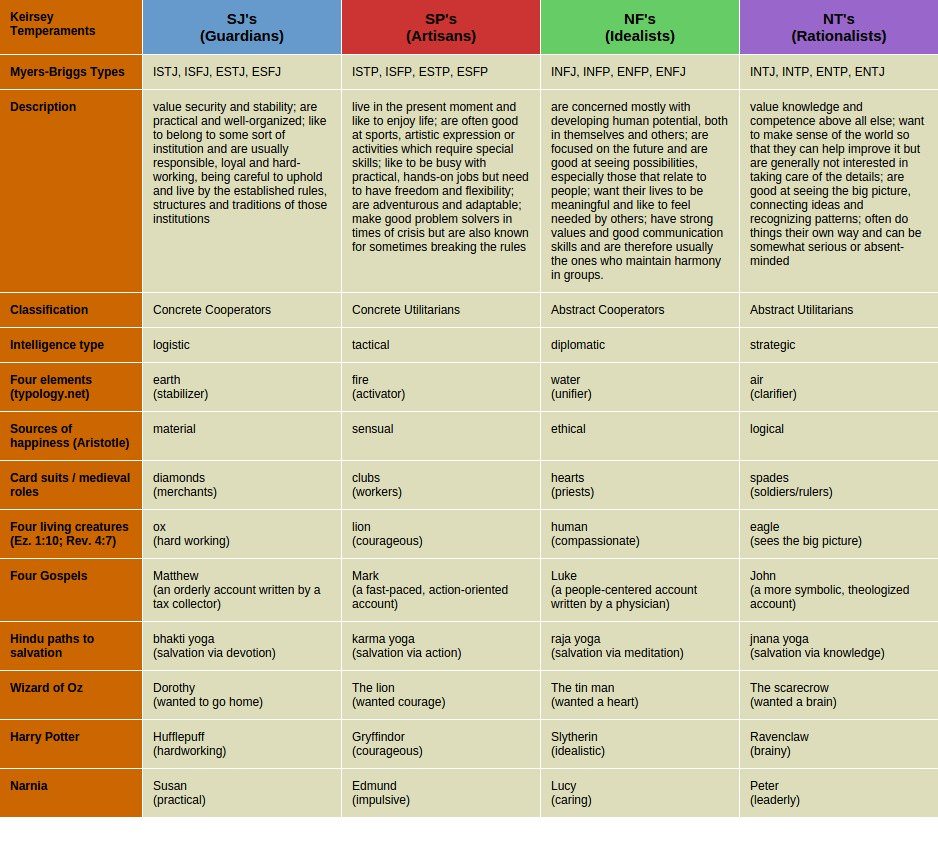
Keirsey Temperaments
David Keirsey expanded on the ancient study of temperament by Hippocrates and Plato. In his works[1], Keirsey used the names suggested by Plato:
- Artisan (iconic)
- Guardian (pistic)
- Idealist (noetic)
- Rational (dianoetic)
Keirsey divided the four temperaments into two categories (roles), each with two types (role variants).
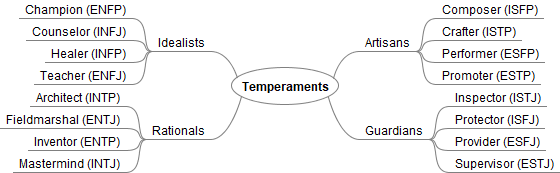
In other words, he took the 16 types and simplified them into 4 temperaments by dividing the S side of the chart into J’s and P’s and the N side into F’s and T’s. The resulting 16 types correlate with the 16 personality types described by Briggs and Myers (MBTI). Furthermore, MBTI is also compatible with the DiSC personality assessment[2].
Finding your personality type
The most common way to find out your type is to take the MBTI personality test. This test requires you to answer questions or statements, as accurately as possible, to determine your type.
Often, these questions require you to rate how well you relate to the question asked as these questions to map your personality type.
For example, such a question may be:
Which answer comes closest to telling how you usually feel or act?
Are you inclined to:
- value sentiment more than logic, or
- value logic more than sentiment?
Do you prefer to:
- arrange dates, parties, etc., well in advance, or
- be free to do whatever looks like fun when the time comes?
Once you’ve taken the test, you can find out how much each personality factor affects your disposition. In the consulting profession, some people may think only certain personalities can be successful. For example, it’s a common belief that only extroverts can engage with and relate to customers.
However, according to research[3], introversion is slightly more common than extroversion. Furthermore, it takes both extroverts and introverts to build a successful engagement team.




